I. INTRODUCTION
II. THE LEGAL STRUCTURE OF BTPLI
III. THE PRACTICE OF THE DUAL MECHANISM OF BTPLI
A. The Legal Mechanism: A Constraint Based on State Power
B. The Reputation Mechanism: Private Constraint of Repeated Game
IV. THE PRACTICAL DILEMMA OF DUAL MECHANISM OF BTPLI
A. The Legal Mechanism
B. The Reputation Mechanism
V. OPTIMIZATION OF THE DUAL GOVERNANCE MECHANISM OF BTPLI
A. The Legal Mechanism
B. The Reputation Mechanism
VI. CONCLUSION
In the governance practice of China’s bankruptcy trustee professional’s liability insurance, a dual governance mechanism with both law and reputation has been initially formed. Law provides behavior patterns and regulation systems for relevant stakeholders, and reputation deters managers from potential illegal activities through market expulsion. However, in this governance mechanism, there are some problems at the legal level, such as the unclear provisions of the bankruptcy trustee’s loyalty obligation and the design of the practice liability insurance clause needs to be improved. At the reputation level, there are some defects, such as insufficient social conditions for the reputation mechanism to play its role and insufficient reputation accumulation of the bankruptcy trustee’s trade associations. Therefore, the standard system of the bankruptcy trustee’s loyalty obligation and trustee’s liability insurance with multiple legal mechanisms, shall solve the problems existing in the legal level, and the defects existing in the reputation level should be resolved by optimizing the social conditions of the reputation mechanism and strengthening the construction of the bankruptcy trustee’s trade association, so that the dual governance mechanism could be enhanced and the Chinese experience could be widely applied across the globe.
I. INTRODUCTION
Supply-side structural reform is a necessary and innovative measure proposed by the Central Economic Working Conference to adapt to and embrace China’s New Norm of economic development. It is increasingly urgent to accelerate the efficiency of resource allocation from the supply-side structural reform. Four related ministries and commissions, including the National Development and Reform Commission issued the report of Key Points for Reducing the Leverage Ratio of Enterprises in 2019 in July 2019, pointing out that the disposal of debts of ‘zombie enterprises’ should be accelerated; the link between corporations and courts in bankruptcy cases should be improved so as to create a sound environment for the disposal of such debts. Meanwhile, the status of the international economy becomes increasingly complicated with the continuous augment of Sino-US trade frictions. Under the influence of these multiple factors, the number of enterprises’ bankruptcy cases has also surged these years. By 2020, under the influence of the sudden outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic, more than 10,000 small and medium-sized enterprises will face bankruptcy at the beginning of the year, and the proportion will continue to increase as the epidemic continues.
The proper disposal of enterprises’ bankruptcy cases is of far-reaching significance to the restoration of social relations damaged by enterprises’ bankruptcy. The responsibilities of the bankruptcy trustee (BT) stipulated in article 25 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law of the People’s Republic of China cover nine parts, such as taking over and handling all aspects of debtor affairs, which play a very important role in the handling of bankruptcy cases. As the number of bankruptcy cases increased, the overall risk of BT’s practice also roared. The liability insurance with the feature of dispersed risks could provide protection for resolving the practicing risks of the BTs to some extent. Therefore, the bankruptcy trustee professional’s liability insurance (BTPLI) has been promoted in many cities and achieved substantial results. As far as BTPLI is concerned, achievements and related issues co-existed. The issue of the confirmation of problems faced by the operation of the relevant legal mechanism and the way of optimizing its operation has become the most urgent problem. Therefore, studying the governance mechanism of BTPLI is of great theoretical value and practical significance.
On the theoretical level, Oliver E. Williamson, winner of the Nobel Prize of Economics in 2009, is called a rediscover of Coase Theorem. Based on Coase’s transaction cost theory, he integrates a large number of interdisciplinary and academic innovations including organizational theory, law and economics, which develop ‘new institutional economics’ into an important branch of contemporary economics. The focus of new institutional economics is the institutional environment and governance structure, in which the institutional environment refers to the formal systems such as property rights system, political system, judiciary and bureaucracy. The governance structure is a governance mechanism focusing on the management of contractual relationship. Williamson divided economics into ‘science of choice’ represented by neoclassical economics and ‘science of contract’ represented by new institutional economics. It shows the position of ‘contract’ in its discipline. The research on the contract governance mechanism has gradually become an important research direction of new institutional economics. Williamson believes that choosing an appropriate governance structure of the contractual relationship can reduce transaction costs and promote cooperative relations. Contract governance is a legal, institutionalized and impersonal mechanism, which can reduce information asymmetry and restrain opportunism by supervising the performance of contract clauses by trading subjects. With the adjustment and change of government functions, the contract is used as a governance tool, and it carries different goals which are applied to different scenarios at different stages. Generally speaking, the research on contract governance is based on dichotomy. That is to say, contract governance is completed through the legal mechanism and private mechanism. Of course, this also includes the third-party executive power represented by trade associations.
Accordingly, scholars divide the contract enforcement mechanism into two types: one is the public enforcement mechanism based on law, and the other is the private enforcement mechanism based on reputation. The meaning of the reputation mechanism contains the interactive relationship between the reputation mechanism and the legal mechanism guaranteed by national coercive force: the legal system based on repetitive relationship, relying on the reputation of self-implementation of both sides of the game and guaranteeing the implementation by national coercive force. Or rely on social norms and lack of a coercive private system to organize and implement, and take contract execution as the center of information disclosure, dispute arbitration, fraud punishment and other rules and procedures. In addition, as far as the complementary relationship between the law and the reputation mechanism is concerned, a sound legal system is a necessary condition to maintain and promote transactions. If there is no law to restrict the execution of contracts, transactions between people will be difficult. The reputation mechanism is a lower-cost mechanism to maintain the order of transactions, and it is even more necessary for the reputation mechanism to work when laws are invalid. Law and reputation are two basic mechanisms to maintain the order of market operation, and many complex transactions need their mutual action. Therefore, based on the structure of contract theory, we should study a specific operating mechanism, by clarifying its legal structure, carrying out research from two dimensions: the legal mechanism and the reputation mechanism as private governance, and analyzing the practical problems existing in its operation on this basis. Based on the dual theoretical framework of law and reputation, this essay analyzed the practice of the BTPLI, the problems of the current mechanism, and provided some ideas for its improvement. It is expected that the common experience of law could provide references for other countries and regions.
II. THE LEGAL STRUCTURE OF BTPLI
The Insurance Law of the People’s Republic of China (Insurance Law), the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law and other relevant laws and regulations have established the institutional basis for the governance of BTPLI in China at the legal level. For example, article 65 of the Insurance Law defines the concept of liability insurance. However, article 24 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law stipulates that an individual who acts as a BT should take part in practicing liability insurance. What kind of institutional framework does the law build? What role does the reputation mechanism play in the operation of BTPLI?
According to article 65 of the Insurance Law and cases in Dongguan, Beijing and other cities, the subject of BTPLI is the liability of the BT’s compensation to creditors, debtors or the third party for the loss caused by the BT (the insured). The insurer shall compensate the third party for the damages caused by the BT (the insured) in accordance with the provisions of the law or the contract. This mechanism based on the insurance contract, on the one hand, reduces the risk of the insured performing the nine responsibilities stipulated in article 25 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law. On the other hand, once the insurance contract is agreed, the insurer will perform the obligation of claim settlement according to the agreement, thus realizing the effective resolution of social contradictions within the framework of the rule of law. It should be noted that in order to simplify the diagram and the length of this essay, it is assumed that the insured and the beneficiary of the insurance are the same entity. Admittedly, there are few exceptions in practice. Both internal and external structures exist in the insurance. The internal structure is based on the insurance contract concluded between the BT (the insured) and the insurance company (the insurer); the external structure contains two levels, among which the first level is the structure of the policyholder (the insured), the insurance company (the insurer) and the third party (see Figure 1).
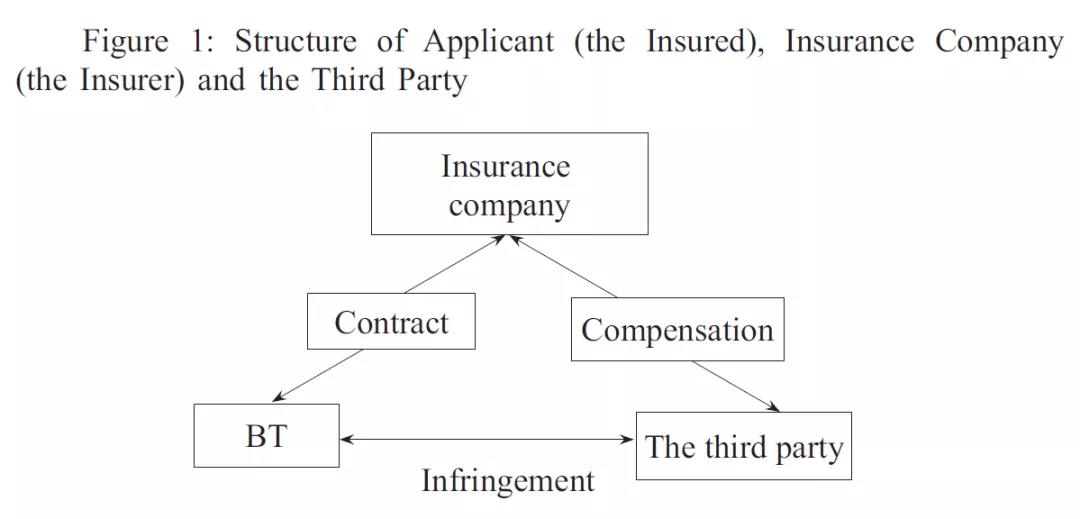
The second level, based on the first one, extends the externalities to the court, creditors and other subjects in the performance of duties of BTs (see Figure 2), which involves industry’s self-discipline and judicial governance. On the surface, the external structure of the second level seems to have no direct relationship with the rights and obligations between the parties to the insurance contract. However, in fact, the external structure of the second level is closely related to whether the BT can perform the nine responsibilities stipulated in article 25 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law prudently and diligently. Without the constraint of the external mechanism, there might be a moral risk caused by non-diligence when a BT believes that ‘there is always an insurance for accidents’.
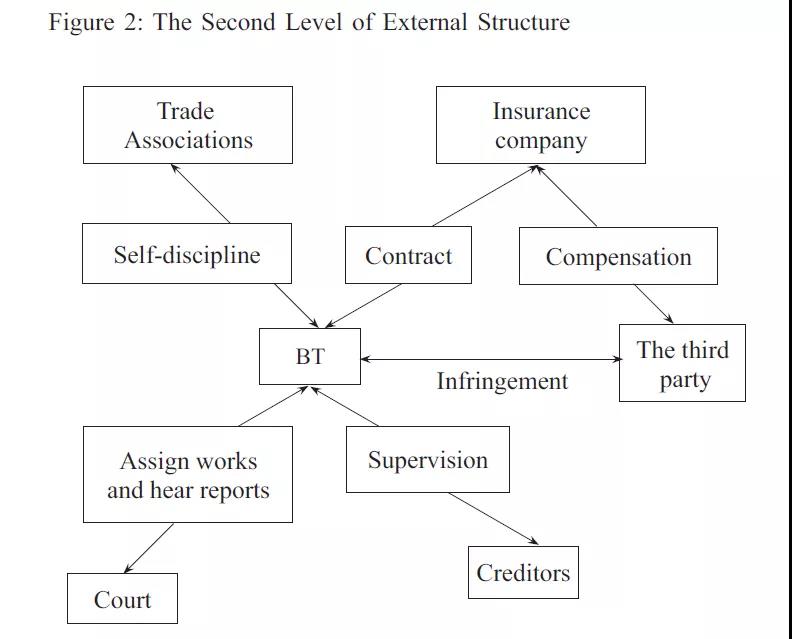
III. THE PRACTICE OF THE DUAL MECHANISM OF BTPLI
The further development of insurance function will provide a more efficient institutional arrangement to achieve social security and stability, and will be fully integrated into the modern social and economic system. Specific to the BTPLI, the contract governance mechanism based on the embedding of the insurance contract is a system output that is fully integrated into the operation of the BT system. Based on the basic structure of BTPLI, the governance mechanism consists of an internal mechanism and an external mechanism. As mentioned above, the research on contractual governance is based on the dichotomy of law and reputation mechanism (private governance). The author observed that the operation practice of BTPLI is subject to the dual constraints of the law and reputation as follows.
A. The Legal Mechanism: A Constraint Based on State Power
Law is an important tool of state governance, and the mechanism of law in contract governance depends on the unified rules of contract law and procedural law. This confirms the principle that the function of the general statement of jurisprudence includes normative function and social function. Specific to BTPLI, law should be regarded as a rule system in this governance mechanism. The normative function of this rule system is embodied in legal norms that can provide relevant stakeholders of the insurance with the practice model, including the judgment and measurement of the legality and efficiency of stakeholders’ behaviors, which enables them to adjust their own behaviors according to the expectations for the legal consequences. It can maintain the relationship and order among stakeholders in BTPLI, providing legal basis and restriction mechanism for related behaviors, and prevent and resolve conflicts and disputes among stakeholders.
With the advancement of the socialist rule of law in China, a relatively stable institutional environment has been provided for the operation of the law. The law has strong credibility, and the relevant subjects form a legal order picture in the operation mechanism of the BTPLI according to the legal norms. This orderly picture depends on the long-term legal construction of the country and the popularization of legal knowledge in the whole society. Of course, this is closely related to the legal expertise of BT, insurance companies, courts, trade associations and other subjects involved in the operation mechanism of manager liability insurance.
1. The Internal Mechanism. — The internal operation mechanism is based on the insurance contract concluded between the BT as the policyholder (the insured) and the insurance company (the insurer). The terms of the insurance contract cover insurance liability, liability exemption, obligations of the insurer, obligations of the policyholder and the insured, compensation, dispute settlement, etc.. In practice, the insurance company draws up the relevant liability insurance clauses of the insurance contract in advance, and then the applicant fills in the application form, which is mainly used to confirm the information of the applicant, the information of the insured, the insurance period, the liability limit and the special agreement. If the applicant wants to modify the insurance clauses in the pre-set model of the insurance company, it should be clearly stated in the special agreement column of the insurance policy. This special agreement needs to be reviewed by the risk control department (in some insurance companies, the legal department performs this duty) within the insurance company, and finally a complete insurance contract is composed of insurance clauses, insurance policies, insurance certificates and approval documents.
This complicated making process of the insurance contract reflects the role of law in the internal mechanism is reflected in two aspects: Firstly, insurance companies are subject to the supervision of the insurance regulatory authorities according to law. If the design of their insurance products, the process of claiming or other procedures violates the law or rules, they shall be subject to administrative penalties. Considering their own compliance costs, insurance companies are inclined to be cautious to avoid the regulatory red line when writing these terms. Under the regulatory constraints, the standardization of insurance companies’ products will be greatly improved. Secondly, for the policyholder (the insured), when entering into the insurance contract, one needs to specify relative terms as accurately as possible, so that the smooth claim can be realized once the insurance accident occurs. When concluding an insurance contract according to relevant laws, the policyholder has the right to require the insurance company to provide sound and standardized terms. And policyholder can stipulate some matters of greatest concern in the special agreement terms. Under these two aspects, the completeness and standardization of insurance contract clauses will be greatly improved.
2. The External Mechanism. — The first level of external mechanism involves the policyholder (the insured), the insurance company (the insurer) and the third party. The role of law in this level is mainly exhibited in three aspects: Firstly, the direct compensation of the insurer (insurance company) to the third party. This mechanism is the legal confirmation of the interests of the third party in the current Insurance Law, but because the third party is not the main body of the insurance contract. Therefore, the insurer can pay directly to the third party only if it is stipulated by law or stipulated in the insurance contract.
Secondly, the third party’s subrogation in specific circumstances. This mechanism presupposes that the insured causes damage to the third party, the liability for compensation is determined, and the insured is slow to request. This system is designed to give the third party the right to claim for payment of insurance benefits under legal conditions.
Thirdly, the lien mechanism of the insurer on the insurance benefit, that is, after the occurrence of liability insurance accident, to prevent the insured from obtaining improper benefits from the accident, the law stipulates that the insurer (insurance company) shall not compensate the insured before the third party obtains actual compensation. These three legal rules are the basis of the allocation of liability insurance rights and obligations. Only on this basis can the external mechanism operate effectively.
The role of the law in the second level of the external mechanism can be found in the following three aspects. Firstly, it provides BTs with restrictions of courts. According to provisions of articles 22, 23, 25, 26, 28 and 29 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, the BT in a bankruptcy case shall be appointed by the court and report to the court the work progress and the scope of its duties. Its employment and resignation shall be approved by the court. Therefore, BTs’ performance is under the supervision of the court with strong legal knowledge reserve, which can effectively limit their improper performance.
Secondly, it enables the supervision of creditors on BTs. Provisions of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law stipulate that the Meeting of Creditors and the Creditor Committee are entitled to the supervision rights on BTs, among which, the most powerful right is that the Meeting of Creditor is in charge of the reviewing of the fees and remuneration of the BT, and it may call for the replacement of the BT. At this level, the supervision and management of creditors can also effectively limit the improper performance of duties by BTs.
Thirdly, it regulates the self-discipline of the trade association. Four related ministries and commissions, including the National Development and Reform Commission issued the report of Key Points for Reducing the Leverage Ratio of Enterprises in 2019 in July 2019, pointing out that the National Association of Bankruptcy Trustees should be established. The Association of Bankruptcy Trustees has not covered the whole country, yet article 24 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law has regulated that law firms, associations and other social intermediary organizations can be appointed as BTs. Having accumulated abundant experience in their own fields, these organizations have already developed their own professional associations, such as the National Law Association. Chinese Law Association and CPA Association implement the compulsory membership system, that is, law firms and lawyers must join the Law Association and accounting firms and certified public accountants must join the CPA Association. The autonomy of professional associations mainly includes the rule-formulation right, the supervision right, the right of punishment, the right of dispute settlement and the right to sue. At least, when law firms and accounting firms act as BTs from the coverage of these associations and the rights vested, the self-discipline system has initially been established in practice. The functions and powers of trade associations in supervision and punishment can restrain the BTs’ performance of duties.
B. The Reputation Mechanism: Private Constraint of Repeated Game
The law has built a strict operating system for the BTPLI. Due to the lag of law and the complexity of daily circumstances, it is impossible for the mechanism construed from the legal framework to provide answers for each specific problem in practice. The initiation of the reputation mechanism which provides the market expulsion punishment in time profoundly affects the core interests of market operators and deters their potential illegal behaviors, is an efficient auxiliary measure of social governance. It is significant for the maintenance of the BTPLI’s operation. Because the BT’s management responsibilities are both procedural and technical, a certain law firm or accounting firm, as a professional intermediary, needs huge time and labor costs to accumulate the BT’s work experience. Therefore, if these professional intermediaries adhere to the short-term psychology of ‘taking one ticket and leaving’; on the one hand, their improper behavior in the process of performing their duties will affect their business opportunities as BT in the future. On the other hand, the cost of accumulating experience will not be converted into subsequent revenue.
Considering their own interests, professional intermediaries will abandon short-term behavior. Instead, they choose to perform their duties as managers diligently and dutifully. In addition, the process of connecting BT with insurance companies, courts and creditors has a long project cycle, and related behaviors have certain repeatability. Therefore, the BT essentially forms a multi-dimensional repeated game relationship in the performance of his duties, which is the basis that the reputation mechanism can become the constraint of his behavior.
1. The Internal Mechanism. — The function of reputation is mainly exhibited in the premium calculation between the two parties of the insurance contract, the policyholder (the insured) and the insurance company (the insurer). When buying insurance from an insurance company, the applicant’s credit will be evaluated through questionnaires or even investigations conducted by lawyers delegated by the insurance company. The content of the questionnaire generally covers the industry, the nature of the firm, the revenue of the applicant and litigation disputes, etc. and it requires the applicant to guarantee that the statement is consistent with the facts and without falsification. If the insurer is liable due to the insured’s breach of the insurance and commitment, the insured is obliged to compensate the insurer. On the other hand, lawyers’ due diligence will disclose the risks of insurance companies signing insurance contracts with policyholders on the basis of the insurance companies’ entrustment scope, the inquiry platforms such as the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System, China Judgment Online and China Executive Information Open Network, the information provided by policyholders and insurance companies, and the relevant lawyers’ practice standards.
The insurance company will comprehensively judge the risk of signing an insurance contract with the insured according to the questionnaire and the lawyer’s report. If no accident happens during the insurance period, the insurer will give a certain discount on premium when renewing the insurance. The reputation of the policyholder before and after insurance will influence the decision-making of the insurer and have obvious constraints on the policyholder. The restrictions of reputation on the insurer are mainly reflected in the efficiency of claims. The intention of a policyholder to purchase insurance is to claim the damages smoothly when the accident occurs, so as to disperse risks. Once the situation where the low efficiency of the claim settlement in that insurer is transmitted to the policyholder, he or she may choose to conclude contracts with other insurance companies after the current one’s expiration. For insurance companies, it is a very direct loss to lose customers because of inefficient claims settlement.
2. The External Mechanism. — The first level of the external mechanism proceeds like the following. The game between the third party and the insurer (insurance company) seems to be one-off. The insurer (insurance company) may encounter the risk of policyholder’s default of the contract if it compensates the third party directly. However, the game between the insurer and the third party is repeated in this level of restriction that is for one specific third party, it is a one-off game, while in the context of the whole market; the insurer may face a variety of third parties. For maximizing profits, insurance companies are inclined to establish and maintain their reputation. Therefore, the rational choice of the insurer is to fulfill the obligation of direct compensation to the third party according to the agreement. This phenomenon coincides with the views of the reputation theorists of enterprises. For an enterprise that takes into account its long-term interests, if it loses the motivation to protect and maintain its reputation, it will no longer be trusted, so the bureaucratic transaction will collapse. Therefore, for the sake of future earnings, enterprises have the power to protect and maintain their reputation.
The second level of the external mechanism contains three aspects. A typical situation in which market punishment mechanism punishes BTs for improper performance of duties is that insurance companies pay compensation to victims for insurance accidents that cause losses to creditors, debtors or third parties. For the BTs, there will be direct fines or loss of premium increase in the next year. In the second level of the external mechanism, the constraints of reputation mechanism on BTs are mainly reflected in the following three aspects. Firstly, the court sets restriction on BTs. The Enterprise Bankruptcy Law has vested the court numerous supervisory functions on BTs. For a single bankruptcy case, the whole process of it provides a suitable environment for repeated game between the court and BTs. In practice, the intermediate court is responsible for compiling the BT’s name list, the rating system, the assessment criteria and others, which extends the scope of repeated game between BTs and the court. It has granted the reputation a stronger constraint for BTs.
Secondly, creditors put constraints on BTs’ reputation. Once entering the bankruptcy liquidation procedure, enterprises are generally faced with complex debts and creditor relationships. Taking the bankruptcy and liquidation case of Company C in City J (county-level city), handled by the author as an example, the structure of creditors is very complex, including private business owners, white-collar professionals, village cadres, civil servants, etc.. The total creditor’s rights are 38,423,395.65 yuan, including a financial institution’s creditor’s rights with the amount of 11,309,233.96 yuan, the social security creditor’s rights of 37,521.48 yuan, the enterprise legal person’s creditor’s rights of 32,800 yuan and 24 private loans of 27,043,840.21 yuan. From the perspective of reputation constraint, the creditor possessing a significant impact on the BT’s reputation is not the financial institution but the 24 private loans with a high proportion of creditor’s rights. Although it is impossible to evaluate creditors’ judgments on the reputation of the BT based on statistics, their evaluation values in the BT’s other activities in the debtor’s city in the future. This urges the BT to perform his duties more prudently and reduce the negative judgment as much as possible.
Thirdly, the reputation restriction is provided by professional association. Trade associations’ self-discipline is a complex governance system, and the autonomy of trade associations comes from authorization law, administrative authorization or contractual authorization. Trade associations give moral restraint to their members mainly through trade self-discipline conventions and non-mandatory spiritual guidance. It can be regarded as an ‘organized private sequence’. As an important form of governance, the realization of self-discipline needs the help of certain independent organizations, namely trade associations. Self-discipline is an important duty of industry associations. Trade associations are the means to realize industry self-discipline. Trade associations manage the market by promoting the collective self-discipline of trade members that is self-discipline. The coverage rate of the Association of Bankruptcy Trustees is not high, and the strong accumulation of reputation system is hard to achieve. However, if the BT is a professional organization such as a law firm or an accounting firm, the reputation accumulation within their own trade association is a good supplement to the BT Association.
IV. THE PRACTICAL DILEMMA OF DUAL MECHANISM OF BTPLI
A. The Legal Mechanism
1. The Vagueness of Provisions of BTs’ Fiduciary Duty.— First and foremost, the question that to whom the BT has the duty of loyalty and diligence has not been clarified. According to article 130 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, Once trustees fail to perform their duties diligently and faithfully in accordance with the provisions of this law, the people’s court may impose a fine; losses caused to creditors, debtors or a third party, should be compensated by them according to law. The article endows the court with the right to fine the trustee for failing to perform his duties diligently and faithfully; meanwhile, it stipulates that the BT’s liability for compensation for the losses of creditors, debtors or the third parties. The trustee has the duty of loyalty and diligence to creditors and debtors, which can be reasonably explained according to the principle of trust relationship in Common Law. However, the requirement of the trustee’s fiduciary duties to the third party is conflicted with the general legal principle. The premise for creditors and debtors to require the trustee’s compensation is his failure to perform his loyalty and diligence, while it cannot be the premise for the third party’s requirements. In order to further clearly apply legal rules in practice, high courts in many Provinces have issued relevant guidelines for handling cases. For example, the Sichuan Provincial Higher People’s Court’s Answers to Several Issues Concerning the Trial of Bankruptcy Cases stipulates that if creditors, debtors and related stakeholders pursue the compensation liability of BT, the premise should be that they perform their duties faithfully and diligently. However, this provision also fails to explain whether the relevant stakeholders are the third party in article 130 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, nor does it clarify whether the BT should undertake the obligation of faithfully and diligently performing his duties for the third party. Theoretically, the nature of the trustee’s liability to creditors and the debtors should be different from that to the third party. Nonetheless, in legislation, the premises of the two are the same. The conflict between legislation and jurisprudence theory is inclined to reduce the clear demarcation of the liability of the trustee to creditors, debtors and the third party.
Secondly, the stipulation of the duty of loyalty and diligence of BTs is too general. Article 27 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law regulates that the BT shall be loyal and diligent in performing his duties. However, there are no specific conditions regulated by the provisions to determine whether the BT has fulfilled the duty of loyalty and diligence or not. A complete insurance contract permitted by law can stipulate what is loyalty and diligence. If the liability insurance contract does not include specific conditions either, it is difficult for the court to confirm the insurance liability in the process of hearing cases. Therefore, we need theory to provide a set of methods for the construction of the standard system of the BT’s duty of loyalty and diligence. And the methodology provided by the theory can be well applied in practice.
2. The Development Level of Liability Insurance Needs to Be Improved. — Firstly, at the macro level of industry development, the scale and level of China’s liability insurance need to be improved. According to the data provided by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners(NAIC), for example in 2018, the total premium income of the US liability insurance business (excluding vehicle liability insurance) was 123.8 billion US dollars, reaching 18.57 percent of the total premium income of the property insurance industry, increasing by 6.41 percent compared with 2017. Compared with the US, there is a big gap between China’s liability insurance business on both absolute and relative scales. In terms of absolute scale, the total premium income of China’s liability insurance in 2018 was 58.899 billion yuan, which only reached 6.8 percent of the income of US liability insurance business (excluding vehicle liability insurance). In terms of relative scale, the premium income of China’s liability insurance accounted for 5.47 percent of the total income of the property insurance industry in 2018, reaching 0.065 percent of the gross national product, far lower than the market share of 18.57 percent and the gross national product share of 0.6 percent in the US. The level of business development and economic contribution of liability insurance in China is low.
Secondly, in addition to the shortcomings of industry development, there are the following specific shortages in the development of BTPLI. For one thing, the design of insurance clause is short of experience. According to the cases handled by the author, the BT’s liability insurance mechanism has been introduced into bankruptcy cases, which has appeared in courts all over the country since 2018. On May 22, 2019, the First Intermediate People’s Court of Beijing issued the Implementation Opinions on Building a Long-Term Mechanism to solve the ‘Difficult Implementation’ by Multiple Measures, which was echoed by the bankruptcy case of Beijing Anpudi Medical Company, when Beijing municipal court introduced the BTPLI system in such cases for the first time. In addition, the Hebei Association of Bankruptcy Trustee actively explored the blanket guarantee of provincial association, which has enhanced the compensation capability of BTs and has been recognized by the court, trade associations, BTs and other stakeholders. However, from the perspective of product design, problems still exist in meeting the actual needs of the insured in various aspects, such as the scope of insurance liability, the insurance period, the insurance liability, liability exemption, insurer’s obligation, policyholder’s obligation, compensation and dispute settlement. All these problems reflect that BTPLI, as a new insurance product, lacks existing cases for reference, and insurance industries around the country are still exploring how to enrich product design. For another, different types of BT have different demands for insurance.
There are two problems for lawyers and accountants being appointed as BTs. The first one is that lawyers and accountants covered by their professional insurance include their daily practice, which is too broad for BTs whose activities are mainly guided by the nine responsibilities. Article 3 of the Articles on Professional Liability Insurance of Lawyers of the People’s Insurance Company of China Limited (approved and filed by the China Insurance Regulatory Commission on September 18, 2009, No. PICC (Filing) [2009] N323) stipulates that ‘within the territory of the People’s Republic of China (except Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan) during the retroactive period or insurance period specified in the policy, the claim of the economic loss of the client due to the insured’s negligence in the course of engaging in litigation or non-litigation business, which should be compensated by the insured shall be compensated by the insurer for the first time.’ This insurance clause is obviously designed for lawyers’ professional activities, but the scope of lawyers’ professional activities is quite different from those that BT may involve. The second is that the insurance amount of professional insurance of lawyers and accountants is limited, which results in the situation where nothing is provided by the insurance during the process of duty performance, once the insurance amount is exhausted in other practice activities. As for liquidation groups, bankruptcy liquidation firms and individuals appointed as the BT, if without similar professional liability insurance of lawyers and accountants, the BTPLI is more suitable for their needs of risk-management. Therefore, it is necessary to design different insurance products for diverse situations where different subjects act as BTs.
B. The Reputation Mechanism
1. The Insufficiency of Social Condition of the Reputation Mechanism. — Theoretically, three social conditions are needed to realize the reputation mechanism: Firstly, information elements. It means that the evaluation of illegal behaviors should enter the information structure of stakeholders and become public information. Secondly, power elements. It means that the stakeholders know the illegal behavior of one party and can make the illegal party suffer losses through their own behavior choices, but there is no necessary connection with the main body of public power. Thirdly, time elements. That is to say, the long-term game formed based on certain organizational arrangements can make criminals punished when they meet again.
In practice, the social conditions for the realization of the reputation mechanism in BTPLI are not sufficient. First of all, as for information elements, in the BT information transmission mechanism, the illegal behavior is effective for those directly related parties, but ineffective for other parties not directly concerned. For instance, for the court accepting bankruptcy cases, the punctuality of insurer’s compensation to the third party cannot be regarded as effective public information. Secondly, as for power elements, it can be seen from Figures 1 and 2 that as the link of the governance mechanism, and sitting in the market competition themselves, both the insurer and the BT have the right to require compensation from the illegal party. From this point of view, the power elements are basically satisfied. Thirdly, as for time elements, the operation of the BTPLI is organic, whose structure denotes the repeated game model among the relevant parties. On the basis of this mechanism, due to the periodicity of bankruptcy cases and the complicated debt relationship of debtors, BTs who do not perform their duties diligently can be punished in repeated games.
2. The Insufficiency of Reputation Accumulation of BT Association. — Both the China Lawyers Association and the China Institute of Certified Public Accountants were founded in the 1980s, which have accumulated rich experience in self-discipline and established relatively comprehensive association regulations and management system. Nonetheless, Guangzhou Association of Bankruptcy Trustee, the first BT Association in China was newly established on November 20, 2014. The first provincial-level enterprise BT association in China, Hebei Enterprise Bankruptcy Administrator Association, was established on November 13, 2015. Compared with the other two, the BT Association is still novel, and the compulsory membership has not been implemented in BT Association. Four related ministries and commissions, including the National Development and Reform Commission issued the report of Key Points for Reducing the Leverage Ratio of Enterprises in 2019 in July 2019, pointing out that the National Association of Bankruptcy Trustees should be established.
From the perspective of cases and policies, BTs’ trade associations will develop rapidly. However, the number of BTs’ trade associations is limited in practice, and there is no national unified guidance and norms. BTs’ trade associations have problems of inexperience in the aspects of association governance, specialty construction, information sharing, resource docking and dispute resolution. This requires strengthening self-construction and gradually accumulating industry governance experience. The reputation mechanism is an important element in the dual governance mechanism of BTPLI, which requires strengthening the role of the reputation mechanism by strengthening the social conditions of the reputation mechanism and building trade associations in practice.
V. OPTIMIZATION OF THE DUAL GOVERNANCE MECHANISM OF BTPLI
A. The Legal Mechanism
1. Improvement of the Standard of BT’s Fiduciary Duty. — The goal of the country’s legislation is to provide the relevant stakeholders of the BTPLI with a behavior pattern, judge and measure the effectiveness of their behavior, so that they can have a clear expectation of the legal consequences of their behavior, so as to maintain the relationship and order among the relevant stakeholders and prevent and resolve the relevant conflicts and disputes.
Due to the lag of law and other reasons, the disconnection between law and practice requires judges to bring their initiative fully into individual cases. The judge shall explain or amend the deficiency of the law by individual judgment. Case guidance system is an effective way for judges to play their initiative. The rules formed by guiding cases can accumulate legislative resources. In addition, based on the close relationship between the guiding cases and the judicial interpretation, the common problems in the guiding cases can be summarized to form the judicial interpretation, so that some prominent problems of the disconnection between the law and the practical needs can be solved in the trial of courts. This essay believes that as for generality of the problem concerning to whom the BT has the duty of loyalty and diligence, one should follow the logic of the guiding cases and judicial interpretation, and improve the standard system of the faithful duty of the BT. Moreover, on the technical level of improving the system, the empirical research on relevant judicial cases helps to sort out the judgment standard of the fiduciary duty in practice. The combination of these experiences under the logic of the judges’ case interpretation, guiding case and judicial interpretation shall form the final judgment standard.
2. The Promotion of the BTPLI with Multiple Legal Measures. — The further development of the BTPLI needs to provide a good legal environment for its operation at the macro level with a legal mechanism. It is also necessary to further summarize the relevant practical experience at the micro level, to combine the actual needs in operation, transforming and promoting the relevant experience, and further segment the product types.
At the macro level of the development of the insurance industry: First of all, local governments can provide BTs with incentives in the form of financial subsidies and tax discounts according to the local financial and tax conditions, so as to increase the insurance coverage rate of BTPLI; aiming at a few insurance companies that lack innovative thoughts which still follow extensive development path. The regulatory authorities should take various measures to promote the transformation of its development model, making these insurance companies contribute to the specialization and differentiation of insurance products, and provide more services and products, to promote the normal development of the industry and provide a good basis for product optimization design.
Second, the banking and insurance regulatory departments at all levels, the insurance trade association and the BT association can highlight the analysis and application of big data, through which they can take the BTPLI as a reference in terms of bank credit loans and financial project to reward positive BTs and balance their insurance expenditure, to provide opportunities for the representative trade associations of bankruptcy administrators and BTs, promote mutual learning among industries, realize the enhancement of their reputation value, and play an incentive effect.
Third, the optimization of the dispute settlement in insurance is necessary, and the enforcement and judicial ability of insurance industry should be stressed to improve the efficiency of dispute settlement. In this way, the legitimate rights and interests of the insured, the insurer and the third party can be protected effectively. In addition, various parties such as regulatory agencies, industry associations, scientific research institutions, insurance companies, policyholders and other parties, can build a dispute resolution mechanism related to interests based on the consensus of cooperation, and promote the non-litigation resolution path of the BTPLI disputes.
At the micro level of insurance product design optimization: First and foremost, one should actively summarize the practical experience of existing cases. On the one hand, summarizing the operation of blanket guarantee’s clauses of Hebei Provincial Association of Bankruptcy Trustee in aspects of insurance liability scope, insurance period, liability exemption, insurer’s obligation, policyholder’s obligation, compensation, dispute settlement and others in practice can provide experience for other regions. On the other hand, the in-depth summary of the association’s experience in terms of the basis, effect, members’ acceptance, the balance between the premium and the profit of the insurance company, the blanket guarantee and the supplementary insurance of the members can provide a reference for the regional BT Association to optimize the self-discipline system in liability insurance.
Secondly, product types should be improved with market demand. According to the objective situation that the experience of BTPLI is insufficient, we can strengthen the product comparison and experience reference of liability insurance in other fields. By comparison, it can provide reference for BTPLI. For example, in the field of safety production liability insurance, the improvement proposal points out: ‘Clarify the difference and complementary relationship between safety liability insurance and existing employment injury insurance. Employment injury insurance has covered regular employees. It is suggested that the life insurance objects of the safety insurance should be the items beyond the coverage of employment injury insurance including the continuous premium paid by the enterprise and the staff with de facto employment relationship. As well as personnel and third parties who enter the construction site for supervision, inspection, visit and guidance due to work relationship. The insurance coverage includes death, disability and medical expenses caused by the insurer. The above expenses shall be compensated by the insurance company within the insurance grade selected by the insured enterprise.’ This provides a good reference for perfecting the relationship between lawyers and accountants, professional liability insurance and BTPLI. When designing the BT’s liability insurance, each insurance company can design the insurance especially for the lawyers and accountants on the basis of the insurance coverage of the insurance company’s existing lawyers and accountants liability insurance. So, as for the situation where lawyers and accountants act as BTs, the complementary relationship between the insurance products and the professional liability insurance should be taken into consideration when designing products. The complementary relation includes the effective supplement of insurance liability and the reasonable increase of insurance amount. For the case when liquidation groups, bankruptcy liquidation firms and individuals are appointed as BTs, the product design should fully consider the risk management and their private consumption preference, since there is no liability insurance similar to that of lawyers and accountants.
B. The Reputation Mechanism
1. The Social Conditions for the Optimization of the Reputation Mechanism. — To guarantee the information circulation mechanism in the BTPLI by the system mechanism so that the inferior information party can obtain the information from the superior party in time. And the illegal information can enter its internal and external mechanisms in time, thus enhancing the effectiveness of the reputation mechanism and providing a good basis for the reputation mechanism to play its role.
Firstly, in the internal mechanism, one should strengthen the insured’s credit investigation, verification and management, and standardize the content of the questionnaire and the terms of the applicant’s commitment and guarantee. The information disclosure and management of insurance associations and insurance companies should be enhanced to make the information a reliable reference of the insured behaviors.
Secondly, in the first level of the external mechanism, the improvement of the management and application of information related to the third party’s direct compensation by the insurance regulatory authorities and insurance associations is in need, which enables the relevant information such as the insurer’s claim settlement efficiency to become the public information that will effectively restrict the insurer. On this basis, the insurance trade association can increase the information of liability insurance claims in the industry’s annual report.
Thirdly, in the second level of the external mechanism, the data sharing mechanism between BTs, courts, creditors and trade associations should be improved, so as to create an environment with more repeated game opportunities for reputation. At present, the Sichuan Provincial Higher People’s Court has been appointed as the authority of the Sichuan Provincial Association of Bankruptcy Trustees, which provides a good opportunity to strengthen the court’s linkage with the BT, creditors and industry associations to promote the reputation mechanism to play its role and create an environment of repeated games. The summary of the pilot experience of the provincial court as the BT authority should be strengthened, so that the pilot experience can provide ideas for the national reform plan. In addition, when the court compiles a register of BTs and implements hierarchical remote management, the relevant information of the BTs’ liability insurance may be used as a reference item for scoring.
2. Strengthening the Construction of Association of Bankruptcy Trustee. — Firstly, the registration system of trade associations of BTs should be optimized. In view of the lack of coverage of the BT trade association, the registration system of the BT trade association should be optimized through the following aspects to promote the construction of the trade association. The first is to optimize the registration restrictions for trade associations and allow the industry of BT representatives to set up trade associations in different professional fields according to actual needs. Second, the competent authorities should strengthen the information disclosure, so that the insurance regulatory authorities can grasp the registration information of trade associations in time and promote a special meeting and work report system with trade associations as the center, and using trade associations as resource intermediaries for communication and interface of bankruptcy related businesses. It provides a good information base for the reputation mechanism to play its full role. Third, to establish an ‘incentive-disciplinary’ co-existence of the bankruptcy administrator trade association operation mechanism. Relevant entities that perform well in the operation of the BTPLI may be subsidized by the government and regulatory agencies and implement trade associations within the exception list system. For BTs who do not participate in the activities of trade associations for a long time and have poor credit status, they can be included in the abnormal list as appropriate, and share information with the regulatory authorities to achieve joint punishment. Gradually a new industry governance model of diversified cooperation between self-discipline management of trade associations and government supervision in the field of BT should be built.
Secondly, the construction of the competent unit of the bankruptcy trustee trade association should be improved. Taking the lawyer association as an example, the Ministry of Justice is in charge of it at the national level, but there is no authority in charge of the association of BT. If the state intends to establish an administrative department for the association in the future, the case of the lawyer association can be regarded as an example. If the state is not inclined to establish such a department, the National Association of BT should fully study the experience of the provincial associations and research results at home and abroad to provide norms and standards for the development of the association. The national association should also be responsible for the assessment and evaluation, and the implementation of the self-discipline system and the punishment system and others. Based on the experience of the Sichuan Provincial Higher People’s Court as the competent authority of the Sichuan Bankruptcy Trustees Association, the development of a self-discipline mechanism at national and local levels should be explored. We can adopt differentiated self-discipline mechanisms at the national and local levels based on the actual situation. Achieving self-discipline in the BT industry can meet governance needs at all levels. Through these methods, the reputation restriction of association of the BT in the process of bankruptcy management can be fully exemplified, and the goal of the steady improvement of BT’s ability as well as the development of the industry can be achieved.
Thirdly, give full play to the main position of BTs’ trade association in the construction of credit system. Market economy is essentially a credit economy, and a good social credit system is the foundation and guarantee for establishing and standardizing the market economic order. Full play to the role of BTs’ trade associations in the construction of credit system should be given, which is of great significance to improve the social foundation of the reputation mechanism of BTPLI. It is necessary to further promote the BTs’ trade associations to establish credit information files, conduct credit information surveys, publicize credit information, and conduct integrity education and training, so as to keep track of the performance of BTs. Through self-discipline mechanisms such as industry rewards and punishments, we can improve the social responsibility awareness of BTs and improve the overall professional level and professional ethics of BTs. Through industry self-discipline, the BT industry can truly achieve ‘survival of the fittest’.
VI. CONCLUSION
Currently, the proper disposal of enterprise bankruptcy cases has become an unavoidable problem. The resolving of relevant cases needs the effective function of the BT’s duties and the reasonable risk-dispersion. In theory, contract governance needs the dual functions of law and reputation mechanism. By applying this theoretical framework to BTPLI, we can see that the law and reputation mechanism construct a dual governance mechanism for BTPLI. BTPLI can be used as an effective mechanism to disperse risks of their professional liability, whose effectiveness depends on the ‘dual governance mechanism’ of law and reputation. The law provides legal basis and restriction mechanism for relevant behaviors of relevant stakeholders, and prevents and solves relevant conflicts and disputes. Its internal mechanism is to regulate and adjust the insurance contract relationship between the insured and the insurance company within the institutional framework of the Insurance Law, the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law and other laws and regulations. On the one hand, it regulates the product design and claims settlement behavior of the insurance company. On the other hand, it ensures the insured can obtain compensation smoothly after the insurance accident. The external mechanism is that the law regulates the rights and obligations among the policyholder, the insurance company and the third party through legal mechanisms such as direct compensation, subrogation and insurance lien, as well as the regulation of the performance of duties of the BT by the courts, creditors and trade associations based on the authorization of laws.
The reputation mechanism, through market-driven punishment, deeply affects the behavior of relevant stakeholders, effectively deterring them from giving up potentially illegal behaviors. The internal mechanism is that the insurer’s premium accounting is used as a medium to judge the reputation of the insured before and after the insurance, to adjust the premium so as to have a binding effect on the insured. The efficiency of claim settlement will influence the policyholder’s choice of insurance company, and the insurance company will affect its business opportunities due to the low efficiency of claim settlement. The external mechanism is that the insurance company is facing a game with some third parties in the market environment. As an enterprise, it will try its best to establish and maintain its reputation out of the consideration of profit maximization. The process of the whole case is complicated and has a long period. The information transmission system of the creditor group, the reputation effect of self-discipline and effective market punishment make the court, creditors, trade associations and the BT form a multi-dimensional game relationship system. On the one hand, it enables the BT to perform the management duties more prudently and reduce the negative reputation evaluation as much as possible. On the other hand, the internal structure of the manager’s liability insurance also plays a role in urging the BT to exercise due diligence and reduce the incidence of insurance accidents.
However, the dual governance mechanism of the BTPLI has difficulties in both legal and reputation aspects. In the legal mechanism, there are some problems, such as the BT has the duty of loyalty and diligence for whom, the rules of the duty of loyalty and diligence of the BT are too principled, the experience of product design is not enough, different types of BT have different needs for practicing liability insurance, etc. On the reputation mechanism, there are some problems, such as insufficient social conditions for the reputation mechanism to play its role and insufficient accumulation of reputation of the trade association of BT. Therefore, we should perfect the standard system of the fiduciary duty of the BT, optimize the product design of the trustee’s liability insurance, and promote the development of the BTPLI with diversified legal mechanisms. On the reputation mechanism, optimize the social conditions of its role, and strengthen the construction of trade association of BT. Only by constantly promoting the innovation of the BTPLI theory and breaking through the limitation of thinking, can the theory guiding the practice and making this insurance play a greater value in practice. This article observes from the experience material, abstracts as far as possible the BTPLI dual governance mechanism practice pattern, and for the existing mechanism existence insufficiency, finds the solution. This paper attempts to promote the theoretical innovation of this insurance, so that the practical experience of this insurance in China can provide experience for other countries and regions in dealing with related issues.

